Dental Exam
New patients receive a comprehensive examination including:
– Check for decayed, fractured, missing and loose teeth
– Evaluate for gum and bone disease
– Take dental x-rays as needed
– Oral cancer exam
– Check overall health and medical history
– Evaluate for routine cleaning or periodontal scaling and root planing(deep cleaning)
A routine dental exam is performed on established patients to determine any changes in dental and health status since the previous visit.
Your gum tissue is measured with a fine instrument ruler to calibrate in millimeters pocket depth between the tooth and the connective gum tissue around the tooth. Pocket depths more than 4 millimeters, could indicate disease and infection. The deeper the pocket, the greater the extent plaque bacteria collects and infection in gum disease develop.
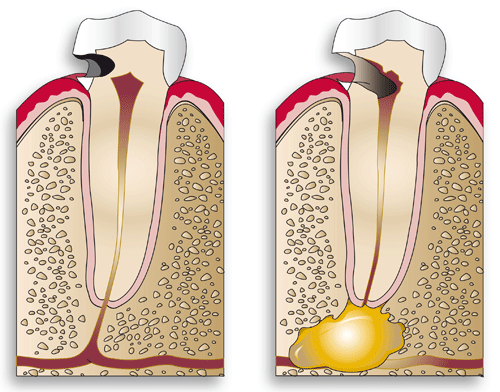
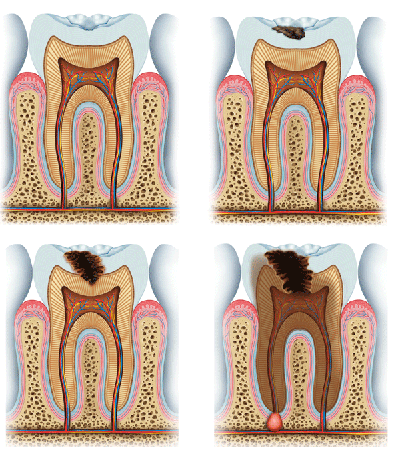
Cavities
Cavities generally develop in the “hard-to-see” places in your mouth. These are normally the places where you need to floss. When bacteria combine with food particles, they form plaque that adheres to your teeth.
As long as plaque remains on the tooth, acid produced by bacteria will eat away the tooth structure. Once through the enamel, the acid attacks the dentin, which is that part of the tooth containing sensitive nerve fibers.
If the tooth decay reaches the dentin, a filling is needed to halt the degenerative process. Otherwise, it continues at an accelerated rate becoming larger and larger.
If not detected and repaired with a filling, the decay can reach the tooth nerve and cause the need for a root canal and/or tooth extraction. With the decay removed and a filling in place the tooth is restored to its original contour.
What causes tooth decay?
There are many causes for tooth decay such as
– Not brushing and flossing your teeth properly and regularly.
– Eating foods high in sugar and carbohydrates such as candy, ice cream, pasta and the like.
– Drinking Sugary drinks such as sodas, juices etc.
These foods and drinks with a lot of sugars and carbohydrates, give the bacteria in your mouth the food it needs to grow. A few other reasons a tooth can become decayed is not getting enough fluoride, not having enough saliva and not seeing a dentist regularly.
To put it in simple terms Tooth decay is caused by acids which are produced by bacteria in the presence of sugar.To prevent tooth decay, these bacteria, sugars and acids must be periodically removed by way of brushing, flossing and routine dental visits.
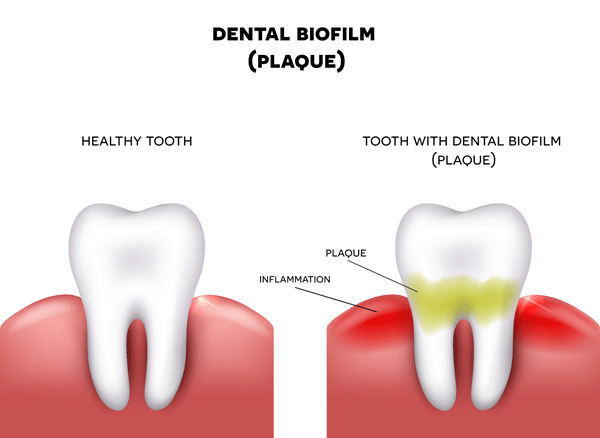
It All Starts With Plaque
Just what exactly is plaque? What causes plaque? What does the dentist recommend you do to prevent plaque from forming?
These are all common and good questions the dentist hears often. Essentially plaque is a soft and sticky film like substance that sticks to your teeth which carries within it tiny bacteria. These bacteria are the main causes of tooth decay as well as gum disease.
Plaque is caused by a build-up from bacteria in the mouth and particles from the foods you eat every day.Once sugars are introduced to plaque, it turns into a tooth eating acid that sits just above the gum line.
Doing your best to avoid plaque build up requires regular oral care including brushing, flossing, oral rinse and routine dental cleanings. Visits to your dentist a couple times a year for check ups and professional dental care will help prevent plaque, gum disease and cavities.
Brushing
If you want to brush your teeth like a professional then start by tilting your tooth brush at a slight angle and move the brush in a rotating motion brushing first the entire face of the teeth all the way up to the gum line.
Next in the same circular motion go across the tops of all of your teeth from front to back followed by the same light brush strokes in a circular motion across the backs of all of your teeth.
Finally brush your tongue in the same fashion as you did your teeth.
Then repeat the process one more time. The entire act of brushing your teeth should take around two minutes and leave your mouth feeling fresh and clean.


Flossing
The dentist recomends you use the following procedure when flossing your teeth.
First break off about 18 inches of floss and wind some of it around your middle finger (3 turns). This finger will take up the floss as it becomes dirty.
Then shorten the length between the two fingers to 6 inches and wind some floss (1 turn) around the opposite middle finger. Hold the floss tightly between your thumbs and index fingers.
Then start at the top of the tooth just at or under the gum line and gently stroke the floss in a downward motion essentially scraping off any leftover particles missed when brushing.Repeat this process on both sides of every tooth
Fluoride
What is Fluoride?
Fluoride is a natural mineral found all over the world and is widely dispersed in nature. There are several foods as well as water supplies that contain fluoride. Sometimes fluoride is added to drinking water to help reduce tooth decay throughout the community. The American Dental Association, the World Health Organization and the American Medical Association, and many other organizations, have and continue to endorse the use of fluoride in community water supplies due to its positive effect on tooth decay.
How Does Fluoride Work?
Fluoride can help prevent cavities in two ways:
First fluoride helps to harden the enamel on teeth both in adults and children making it more difficult for decay and cavity causing issues.
Second when eating your saliva produces acids that cause “demineralization” which is a dissolving of the calcium and phosphorous beneath the tooth’s surface and when your saliva is less acidic due to lack of stimulation it replenishes that same calcium and phosphorus which is called “reminerlization”. When fluoride is present and active through the remineralization process, the minerals that are being deposited are harder than they would have been otherwise, strengthening your teeth and helping to prevent deterioration during the next demineralization phase

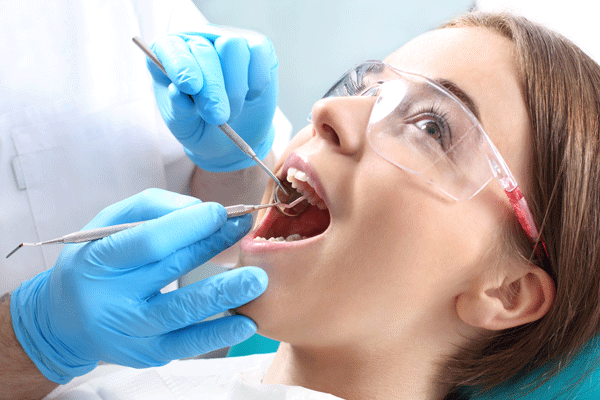
Tooth Scaling
Tooth scaling removes plaque, tartar and hard crusty calculus deposits, which are loaded with bacteria.
Root Planing
After scaling the tooth roots may need to be planed to smooth the root surface. Soft tissue will re-attach itself to a smooth tooth surface.
Sealants
Sealants are a proven way to help prevent cavities. Although sealants do not take the place of proper oral hygiene, they do prevent bacteria from getting into the deeper crevices in a tooth’s biting surface and therefore keeping the tooth cavity-free.
Contact Info
La Puente Family Dental Center
15321 Elliot Ave.
La Puente, CA 91744
(Near Donut Hole & Post Office)
Office Hours
Mon - Fri: 9:00 am to 6:00 pm
Closed: Saturday & Sunday

